NASA launched the primary 5 full-colour photographs from the James Webb House Telescope on Tuesday, July 12. The world’s strongest house telescope has captured the picture of a galaxy cluster because it appeared billions of years in the past, detected the presence of water on an exoplanet, revealed distinctive particulars of the ‘Eight-burst Nebula’, make clear galaxy evolution and black holes, and unveiled ‘Cosmic Cliffs’ within the Carina Nebula.
The President of the US, Joe Biden, unveiled the deepest and the sharpest infrared picture of the distant universe thus far. This was the primary full-colour picture to be launched from Webb.
NASA quietly launched two extra Webb photographs. These are the pictures of Jupiter, the Jovian moons Europa, Thebe and Metis, and the fuel large’s ring. The photographs have been captured whereas Webb was being examined, and have been offered within the JWST commissioning report.
Webb’s full-colour photographs reveal a number of secrets and techniques in regards to the cosmos.
Page Contents
Webb’s First Deep Area: Deepest Picture Of Early Universe
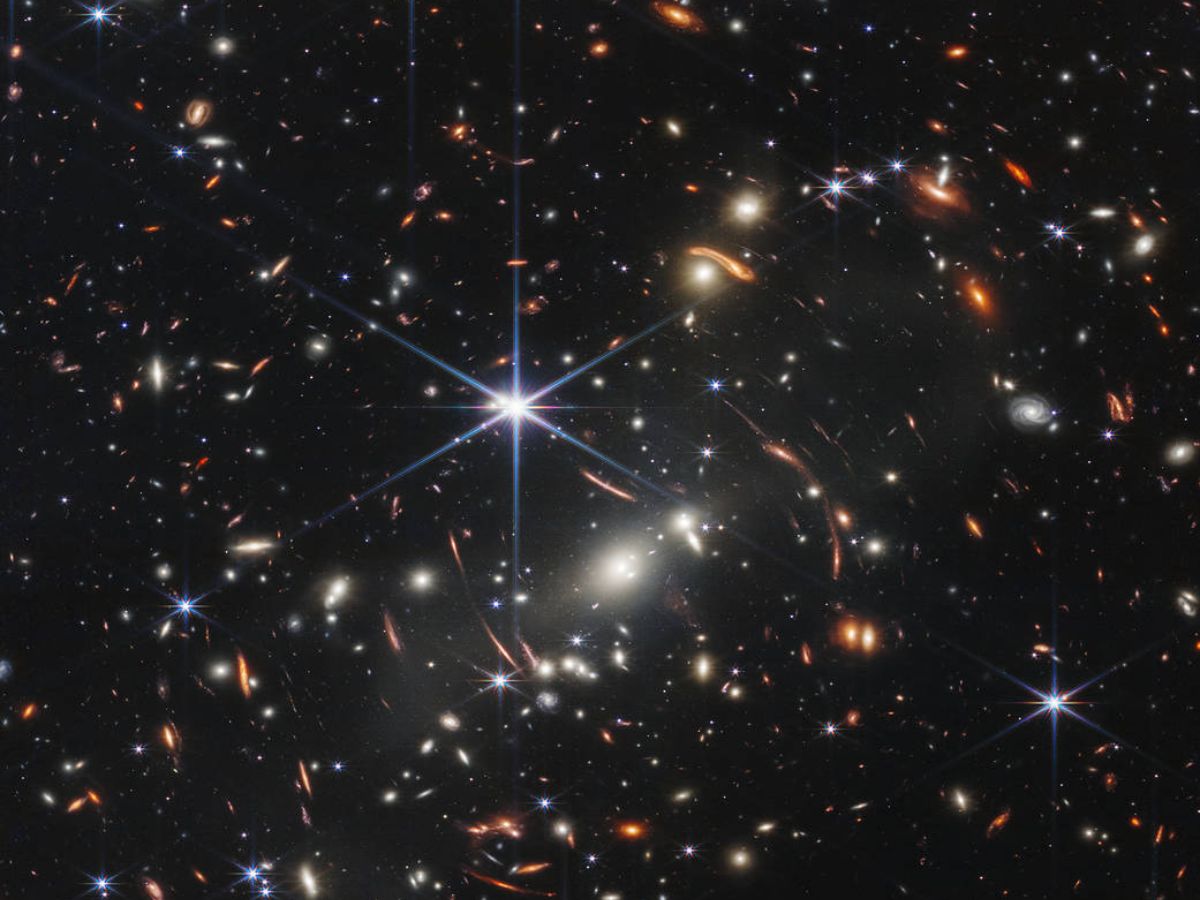

The deepest and sharpest infrared picture of the distant universe thus far is named Webb’s First Deep Area. That is a picture of the galaxy cluster SMACS 0723, and is “overflowing with element”, based on the European House Company. The galaxy cluster is current close to the constellation Volans within the southern sky.
Hundreds of galaxies and the faintest objects ever noticed in infrared gentle have appeared in Webb’s view.
The picture has been captured by Webb’s Close to-Infrared Digicam (NIRCam), and is a composite constituted of photographs at completely different wavelengths, totalling 12.5 hours. In keeping with NASA, the mixed mass of the galaxy cluster SMACS 0723 acts as a gravitational lens, magnifying extra distant galaxies. The highly effective gravitational subject of the galaxy cluster bent the sunshine rays from the distant galaxies behind it, just like a magnifying glass.
Among the galaxies are from the early universe, when the universe was lower than a billion years previous.
Webb’s First Deep Area reveals the galaxy cluster SMACS 0723 because it appeared 4.6 billion years in the past. The NIRCam instrument has introduced distant galaxies into sharp focus. These galaxies have tiny, faint constructions which have by no means been seen earlier than, together with star clusters and diffuse options.
It took billions of years for the sunshine from these galaxies to achieve us. When viewing the youngest galaxies in Webb’s First Deep Area, we’re wanting again in time to some 100 million years after the Large Bang. Because of the enlargement of the universe, the sunshine was stretched to infrared wavelengths that Webb was designed to watch.
Webb has additionally captured stars, which seem brighter at shorter wavelengths.
The galaxy cluster has additionally been captured by Webb’s Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI). The MIRI picture provides a kaleidoscope of colors and highlights the place the mud is current. Mud is a significant ingredient for star formation, and finally for all times.
Blue stars comprise stars, however little or no mud, whereas pink objects are made up of thick layers of mud. Inexperienced galaxies comprise hydrocarbons and different chemical compounds.
The info from Webb’s Close to Infrared Spectrograph (NIRSpec), which noticed 48 particular person galaxies on the similar time, revealed gentle from one galaxy that travelled for 13.1 billion years earlier than Webb’s mirrors captured it.
WASP-96 b: Webb Detects Water In An Exoplanet’s Ambiance
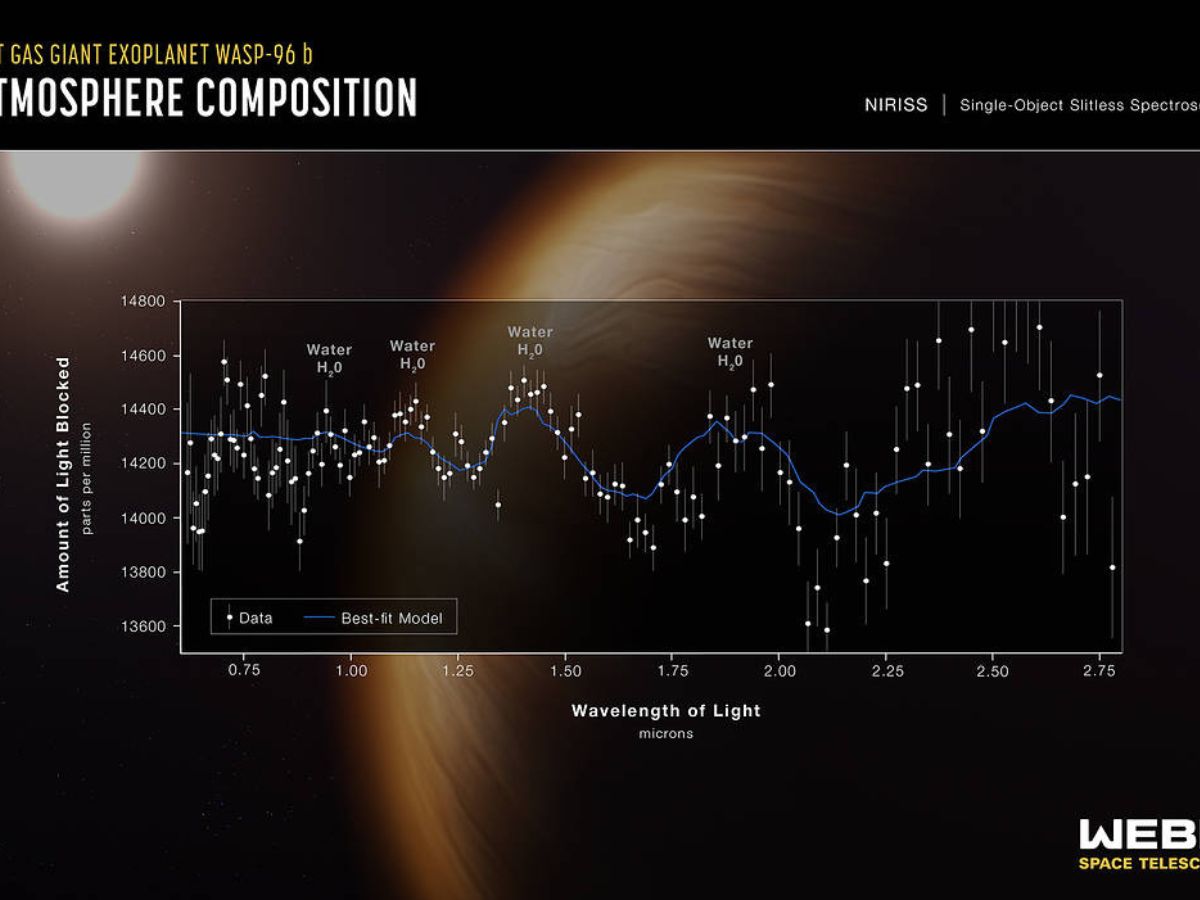
Webb has imaged the distinct signature of water, together with proof for clouds and haze, within the environment surrounding a scorching, puffy, fuel large planet. The planet is orbiting a distant Solar-like star. Webb has revealed the steamy environment of the distant planet intimately.
Webb’s monumental mirror and exact devices have captured essentially the most detailed measurements of starlight filtering by means of the environment of WASP-96 b, an exoplanet.
In keeping with NASA, the spectrum of sunshine, which accommodates details about the make-up of a planetary environment 1,150 light-years away from Earth, reveals the distinct signature of water.
Webb’s detailed commentary of the environment of an exoplanet marks an enormous leap ahead within the seek for doubtlessly liveable planets past Earth.
The picture of the exoplanet was captured by the Close to-infrared imager and slitless spectrograph (NIRISS), an instrument on Webb.
The JWST has detected the presence of particular fuel molecules based mostly on tiny decreases within the brightness of exact colors of sunshine.
In keeping with NASA, this commentary is the “most detailed of its type thus far”, and demonstrates Webb’s capacity to analyse atmospheres lots of of sunshine years away.
WASP-96 b, certainly one of greater than 5,000 confirmed exoplanets within the Milky Manner, is positioned within the southern-sky constellation Phoenix. The exoplanet is a sort of fuel large with none direct analogue within the photo voltaic system, and has a mass lower than half that of Jupiter, and a diameter 1.2 occasions higher.
With a temperature higher than 1000 levels Fahrenheit, WASP-96 b is considerably hotter, and orbits extraordinarily near its Solar-like star, at simply one-ninth the space between Mercury and the Solar.
The exoplanet is a perfect goal for atmospheric observations due to the mixture of huge dimension, brief orbital interval, puffy environment, and lack of contaminating gentle from objects close by within the sky.
On June 21, Webb’s NIRISS measured gentle from the WASP-96 b system for six.4 hours because the planet moved throughout the star, and in consequence, a lightweight curve and a transmission spectrum have been obtained. Because the exoplanet transits the star’s disc, its gentle dims.
The sunshine curve confirms properties of the exoplanet that had beforehand been decided from different observations, and the transmission spectrum reveals beforehand hidden particulars of the environment, together with the unambiguous signature of water, indications of haze, and proof of clouds that weren’t thought to exist.
By evaluating the starlight filtered by means of a planet’s environment because it strikes throughout the star to the unfiltered starlight detected when the planet is beside the star, researchers made a transmission spectrum. The NIRISS is essentially the most detailed exoplanet spectrum thus far.
In keeping with NASA, the spectrum will assist researchers measure the quantity of water vapour within the environment, decide the abundance of assorted components like carbon and oxygen, and estimate the temperature of the environment with depth. Utilizing this data, researchers can decide the general make-up of the planet, and know the way, when, and the place it shaped.
Webb’s 270-square-foot gold-coated mirror collects infrared gentle effectively. The commentary made by NIRISS demonstrates that Webb has the facility to characterise the atmospheres of exoplanets, together with these of doubtless liveable planets, in beautiful element.
Southern Ring Nebula: How A Dying Star Behaves
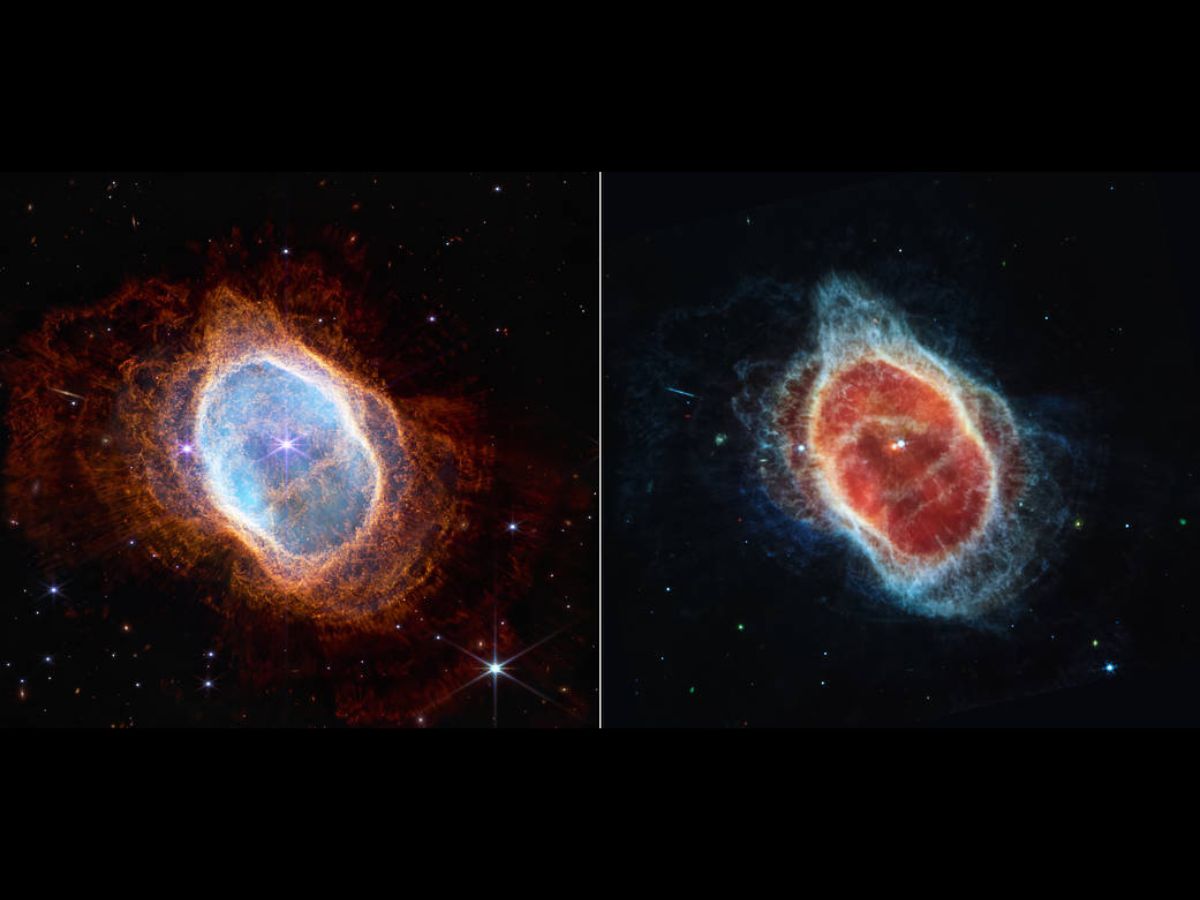

Webb’s third picture to be unveiled is that of the Southern Ring planetary nebula or the “Eight-burst Nebula”. The nebula is roughly 2,500 gentle years away from Earth.
In keeping with NASA, planetary nebulae are the shells of fuel and dirt ejected from dying stars.
By its third full-colour picture, Webb has revealed particulars of the Southern Ring planetary nebula that have been beforehand hidden from astronomers. Shells of fuel and dirt ejected from dying stars represent planetary nebulae.
The highly effective infrared view of Webb has introduced the nebula’s second star into full view, together with distinctive constructions created as the celebrities form the fuel and dirt round them. The infrared view of the telescope additionally reveals particulars of the distinctive constructions created as the celebrities form the fuel and dirt round them.
In keeping with NASA, new particulars from the late phases of a star’s life will assist the world higher perceive how stars evolve and remodel their environments. The picture has captured the “ultimate efficiency” of a dying star in nice element.
A cache of distant galaxies may also be seen within the background. A lot of the multi-coloured factors seen within the picture are galaxies, not stars.
The Southern Ring planetary nebula has been imaged utilizing the Close to-Infrared Digicam (NIRCam) and the Mid Infra-Purple Instrument (MIRI).
Two stars, locked in a decent orbit, form the native panorama of the cosmic entity. The picture from Webb’s NIRCam (left) reveals the celebrities and their layers of sunshine. In the meantime, the picture from Webb’s MIRI (proper) reveals for the primary time that the second star is surrounded by mud.
A whole bunch of stars and background galaxies are seen within the near-infrared picture, whereas dusty planet-forming disks round younger stars are seen within the mid-infrared picture.
In keeping with NASA, the brighter star, which is in an earlier stage of its evolution, will in all probability eject its personal planetary nebula sooner or later.
The brighter star influences the looks of the nebula. As the 2 stars orbit each other, they “stir the pot” of fuel and dirt. This causes asymmetrical patterns.
The dimmer star seen on the centre of the nebula has been sending out rings of fuel and dirt for 1000’s of years in all instructions, and Webb has revealed for the primary time that the star is cloaked in mud.
In keeping with NASA, every shell of fuel represents an episode the place the fainter star misplaced a few of its mass. The widest shells of fuel, seen towards the outer areas of the nebula, have been ejected earlier. The shells of fuel closest to the star and the newest. By tracing these elections, researchers can look into the historical past of the system.
NIRCam has additionally made observations which reveal extraordinarily nice rays of sunshine across the planetary nebula. There are holes within the fuel and dirt from which starlight streams out.
In keeping with NASA, observing a nebula is like watching a film in exceptionally sluggish movement as a result of planetary nebulae exist for tens of 1000’s of years. The shells of fuel puffed by the star give researchers the flexibility to exactly measure the fuel and dirt current within the planetary nebula.
Mud and molecules type throughout the shells of fabric ejected by the star. This modifications the panorama even because the star continues to expel materials. The mud ultimately enriches the areas round it, and expands into the Interstellar medium. The mud could be very long-lived, due to which it could find yourself travelling by means of house for billions of years and turn into included into a brand new star or planet.
The fragile layers of fuel and dirt seen within the Southern Planetary Nebula will dissipate into surrounding house in 1000’s of years.
Stephan’s Quintet: Webb Captures Dancing Galaxies
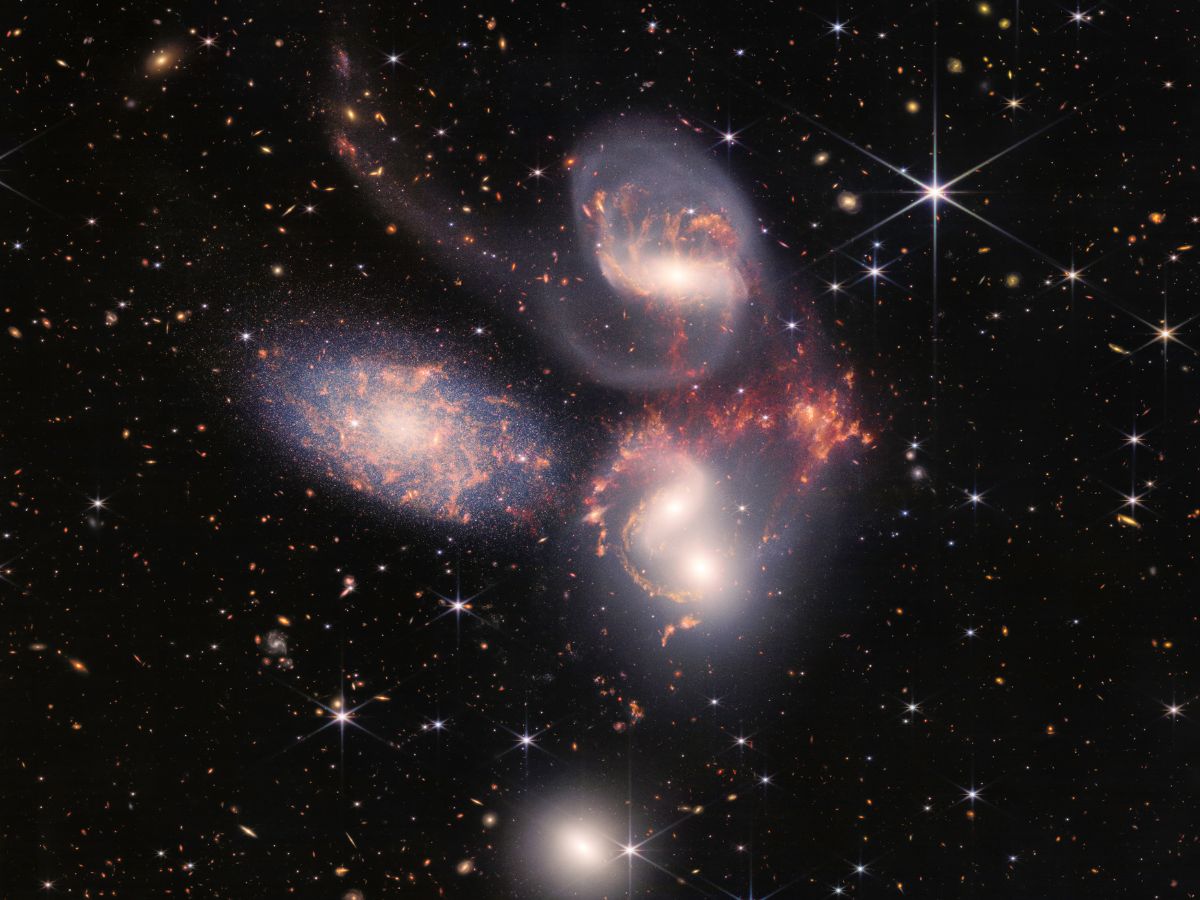

The fourth full-colour picture is that of a galaxy group known as “Stephan’s Quintet”. By its fourth full-colour picture, Webb has revealed never-before-seen particulars of Stephan’s Quintet. This visible grouping of 5 galaxies was prominently featured within the basic movie, “It is a Fantastic Life”.
Because of the shut proximity of Stephen’s Quintet, astronomers can see galactic mergers and interactions. The picture reveals in uncommon element how interacting galaxies set off star formation in one another and the way fuel in galaxies is being disturbed.
Webb has revealed never-before-seen particulars of a galaxy group known as “Stephen’s Quintet”. Because of the shut proximity of Stephen’s Quintet, astronomers can see galactic mergers and interactions.
Stephan’s Quintet was found by the French astronomer Édouard Stephan in 1877. It’s positioned within the constellation Pegasus.
Webb’s fourth picture reveals in uncommon element how interacting galaxies set off star formation in one another.
In keeping with NASA, Webb’s picture reveals outflows pushed by a black gap in Stephan’s Quintet in a stage of element by no means seen earlier than.
The early universe was superheated, on account of which infalling materials might have fuelled very energetic black holes known as quasars. Additionally, tight galaxy teams like Stephan’s Quintet are prone to have been extra widespread within the early universe.
The large mosaic of Stephan’s Quintet is the biggest picture thus far from the Webb House Telescope. It accommodates over 150 million pixels and is constructed from virtually 1,000 separate picture information, and offers new insights into how galactic interactions might have pushed galactic evolution within the early universe.
The MIRI and NIRCam devices captured the visible grouping of the 5 galaxies of Stephan’s Quintet. Collectively, the galaxies are often known as the Hickson Compact Group 92.
The galaxies in Stephan’s Quintet are in a galactic dance with one another. The picture sheds gentle into galaxy evolutions and black holes.
Webb’s image reveals glowing clusters of hundreds of thousands of younger stars and starburst areas of recent star beginning.
On account of gravitational interventions, sweeping tails of fuel, mud and stars are being pulled from a number of of the galaxies. Webb has captured big shock waves as one of many galaxies, NGC 7318B, smashed by means of the cluster.
Solely 4 of the galaxies in Stephan’s Quintet are actually shut collectively and caught in a cosmic dance. NGC 7320, the fifth and leftmost galaxy, is within the foreground, in contrast with the opposite 4. The galaxy is current 40 million light-years away from Earth. In the meantime, the opposite 4 galaxies — NGC 7317, NGC 7318A, NGC 7318B, and NGC 7319 — are about 290 million light-years away from Earth.
In keeping with NASA, this distance is pretty shut in cosmic phrases, in contrast with extra distant galaxies billions of light-years away. Scientists can higher perceive constructions seen in a way more distant universe by learning such comparatively close by galaxies.
Scientists hardly ever get the chance to see intimately how interacting galaxies set off star formation in one another, and the way the fuel in these galaxies is being disturbed. In keeping with NASA, Stephan’s Quintet is a unbelievable “laboratory” for learning these processes basic to all galaxies.
NGC 7319, the topmost galaxy within the group, harbours an energetic galactic nucleus, which is a supermassive black gap 24 million occasions the mass of the Solar. The energetic galactic nucleus is actively pulling in materials and places out gentle power equal to 40 billion Suns.
Utilizing the Close to-Infrared Spectrograph (NIRSpec) and MIRI, Webb has studied the energetic galactic nucleus in nice element. The devices helped the Webb staff get hold of a set of photographs of the galactic core’s spectral options.
The telescope pierced by means of the shroud of mud surrounding the nucleus to disclose scorching fuel close to the energetic black gap and measure the rate of vivid outflows, and noticed the outflows pushed by the black gap in unprecedented element.
Webb was capable of resolve particular person stars in NGC 7320 and in addition the galaxy’s vivid core.
The JWST revealed an enormous sea of 1000’s of distant background galaxies as a bonus.
Probably the most detailed picture of the Stephan’s Quintet, together with Webb information, will assist scientists perceive the speed at which supermassive black holes feed and develop, and to see star-forming areas extra instantly.
Cosmic Cliffs: Glittering Panorama Of Starbirth
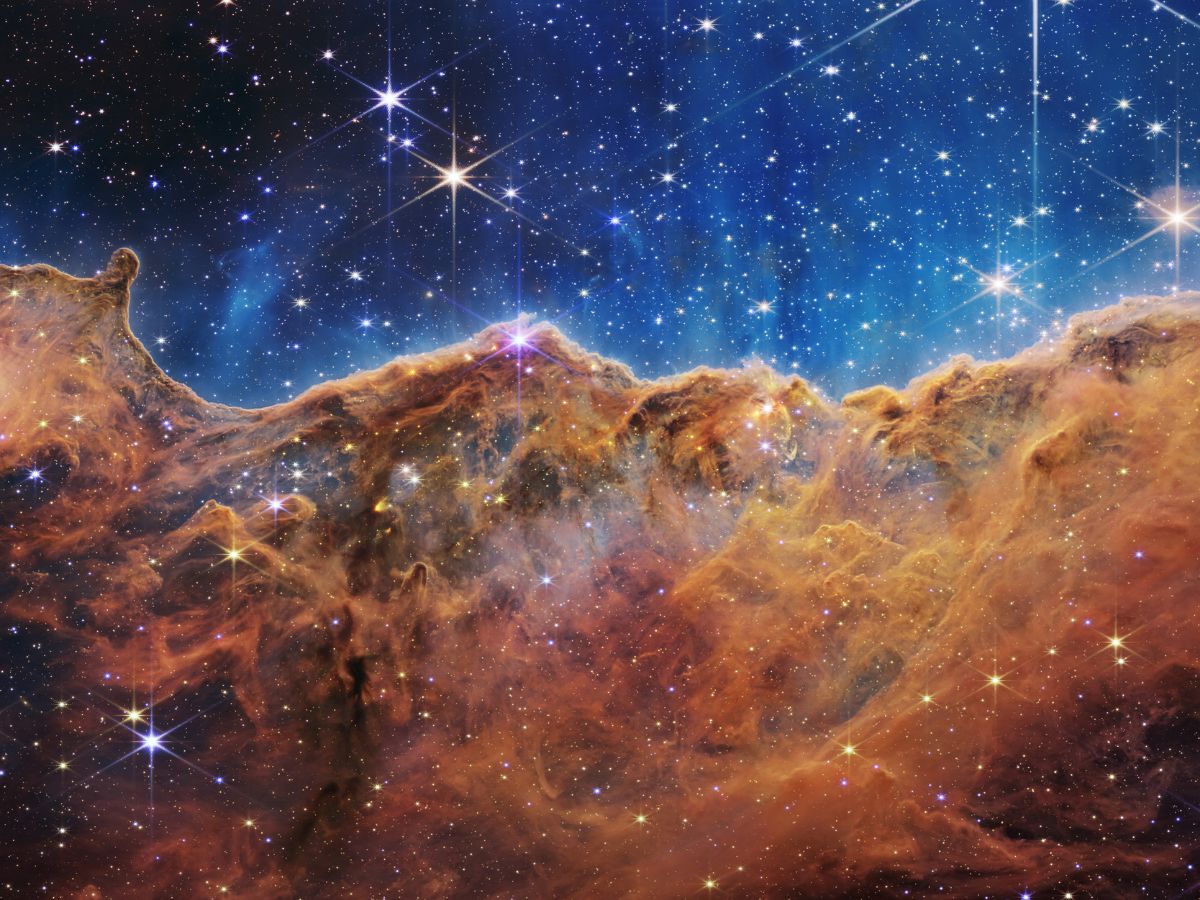

The fifth and ultimate full-colour picture captured by the James Webb House Telescope is that of the Carina Nebula. The picture reveals child stars within the Carina Nebula, the place ultraviolet radiation and stellar winds form colossal partitions of mud and fuel.
Webb’s fifth and ultimate full-colour picture reveals rising stellar nurseries and particular person stars within the Carina Nebula.
The picture is named “Cosmic Cliffs”, and is a seemingly three-dimensional image. A panorama of “mountains” and “valleys” speckled with glittering stars will be seen within the picture.
The panorama is the sting of a close-by, younger star-forming area known as NGC 3324 within the Carina Nebula. Webb has captured the picture in infrared gentle.
“Cosmic Cliffs” reveals for the primary time beforehand invisible areas of star beginning. The picture reveals the “glittering panorama” of star beginning.
Webb’s excessive sensitivity, spatial decision, and imaging functionality helped seize the cosmic objects within the earliest, speedy phases of star formation.
NGC 3324 is positioned roughly 7,600 light-years away from Earth. Webb’s NIRCam and MIRI captured the star-forming area. The tallest peaks seen within the picture are about seven light-years excessive.
On account of intense ultraviolet radiation and stellar winds from extraordinarily large, scorching, younger stars, a cavernous space has been carved from the nebula. The younger stars are positioned within the centre of the bubble. The celebs will be seen within the prime of the picture.
Webb’s NIRCam instrument has unveiled lots of of beforehand hidden stars, and even quite a few background galaxies.
MIRI has revealed the constructions which might be embedded within the mud and uncovered the stellar sources of large outflows.
In keeping with NASA, the blistering, ultraviolet radiation from the younger stars is sculpting the Carina nebula’s wall by slowly eroding it away. Pillars resisting this radiation tower above the glowing wall of fuel.
A “steam” seems to rise from the celestial “mountains”. The steam is definitely scorching, ionised fuel and scorching mud streaming away from the nebula because of the blistering ultraviolet radiation.
By its infrared imaginative and prescient, Webb reveals rising stellar nurseries and particular person stars which might be fully hidden in visible-light footage. Webb can peer by means of cosmic mud to see objects due to its sensitivity to infrared gentle.
Protostellar jets, that are intriguing signspots of star formation, will be seen within the picture. These jets shoot out from a few of the younger stars.
The youngest stars seem as pink spots at nighttime, dusty area of the cloud, based on NASA.
Webb’s observations of NGC 3324 will make clear the method of star formation. The beginning of a star propagates over time, and is triggered by the enlargement of the eroding cavity.
The intense, ionised rim strikes into the nebula, and slowly pushes into the fuel and dirt.
The stress within the rim might enhance if it encounters any unstable materials. It will set off the fabric to break down and type new stars.
Nonetheless, the identical disturbance might stop star formation. It’s because the star-forming materials is eroding away. In keeping with NASA, this can be a very delicate stability between sparking star formation and stopping it. Among the questions of recent astrophysics which Webb will reply embrace what determines the variety of stars forming in a sure area and why stars type with a sure mass.
Different data which Webb will unveil embrace the affect of star formation on the evolution of gigantic clouds of fuel and dirt. Low-mass stars create slim, opposing jets as they type. This injects a whole lot of momentum and power into the clouds of fuel and dirt, lowering the fraction of nebular materials that seeds new stars.
Webb’s NIRCam, which has crisp decision and unparalleled sensitivity, has unveiled lots of of beforehand hidden stars, and quite a few background galaxies.
Younger stars and their dusty planet-forming disks have appeared in MIRI’s view. These discs shine brightly within the mid-infrared, and seem pink and pink. MIRI has revealed constructions embedded within the mud, and has uncovered the stellar sources of large jets and outflows.
Scottish astronomer James Dunlop was the primary to catalogue NGC 3324. The star-forming area is positioned on the northwest nook of the Carina Nebula, which resides within the constellation Carina.
The Keyhole Nebula, and the energetic, unstable supergiant star known as Eta Carinae are additionally current within the Carina Nebula.
Jupiter, Its Moons, And Ring
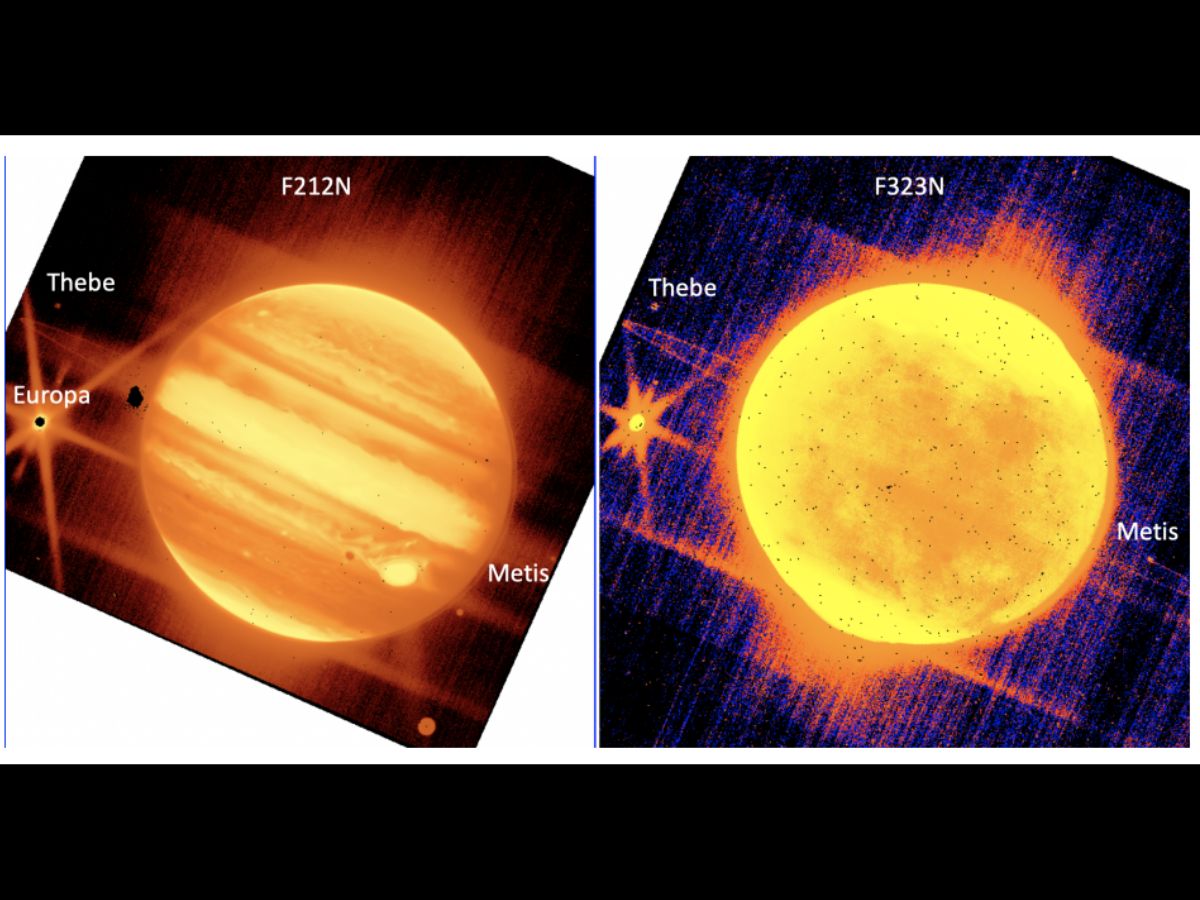
Webb has tracked photo voltaic system objects at speeds greater than twice the requirement. The telescope has detected faint galaxies and noticed targets as vivid as Jupiter.
The telescope tracked Jupiter utilizing devices akin to NIRCam, NIRISS (Close to-Infrared Imager and Slitless Spectrograph), and the MIRI MRS (medium-resolution spectrometer).
Considered one of Webb’s programmes demonstrated that the telescope can monitor transferring targets even when there’s scattered gentle from a vivid Jovian planet.
The NIRCam instrument captured two photographs of Jupiter. One of many footage is a short-wavelength picture whereas the opposite is a long-wavelength picture.
In each the pictures, the Jovian moons Europa, Thebe and Metis will be seen. The shadow of Europa can also be seen, simply to the left of the Nice Purple Spot on Jupiter. The fuel large’s ring is faintly seen within the Webb photographs.
The JWST is a global collaboration between NASA, European House Company (ESA) and the Canadian House Company (CSA). After many years of wait, Webb was launched into house on December 25, 2021, atop an Ariane 5 rocket from the Guiana House Centre positioned close to Kourou, French Guiana.
Webb will look at each section of cosmic historical past, from the primary luminous glows after the Large Bang to the formation of galaxies, stars, and planets, and the evolution of our personal photo voltaic system.












Leave a Comment