On-Page SEO Measures: SEO is a term used regularly by those responsible for online marketing and is often associated with off-page optimization. Both terms describe the search engine optimization of your own website.
Through targeted SEO optimization, your own website should rank better with the search engines, generate more traffic, and ultimately lead to more conversions or leads.
As a rule, those responsible for marketing only know a part of the measures that can be carried out.
In this article, we explain what Onpage SEO is all about and give you initial tips on how to implement it in practice. You will come across different spellings on the Internet, but they always mean the same thing.
Possible formulations are Onpage SEO, Onpage Optimization, Onpage Optimization, On-Page Optimization, SEO Onpage, SEO Optimization, or Onsite Optimization.
Page Contents
On-page Analysis – The first step in on-page SEO

At the beginning of the work, you should do an on-site analysis of the entire website. Here you first analyze the technical SEO in order to identify possible technical pitfalls that influence the crawling of the website. In the next step, check the content of the website in order to be able to carry out content optimization.
After you have examined both areas, you can derive a prioritized catalog of measures from them, which you then implement step by step.
To follow the development of your website in SEO, you can use Google’s Google Search Console. This represents an interface between the website operator and Google and shows which URLs rank well, for which keywords the domain is found, and where there are problems on the website. It also shows graphically how often the individual pages are displayed on the Google search results page.
Technical SEO – the foundation of on-page optimization
Before you can start optimizing your content, your technical SEO must be implemented correctly. This is the only way to ensure that the website can be easily crawled by the search engines and that all content can be read and processed properly.
If the technical SEO is not implemented correctly, it can happen that content optimization, the so-called content optimization, does not work properly because the search engines have no access to the content. Technical SEO is therefore the foundation of every SEO on-page optimization.
Crawling – can the search engine reach your website?

Crawling is only about accessing content and has nothing to do with indexing. Search engines like Google do crawl pages but do not index them. This can be for a variety of reasons, including poor search engine optimization.
In order to improve the relevance of the content, however, only the content should be made crawlable that is absolutely to be processed by the search engines. Unimportant pages such as search result pages or the imprint should therefore be excluded from crawling.
Here one speaks of the optimization of the so-called crawl budget. This defines how many pages on a website can be crawled and are set individually by search engines for each domain.
In this context there is an important distinction:
Crawling is not the same as indexing!
Use the meta tag “robots” and the “robots.txt” file to control crawling. With the “robots.txt,” it should be noted, however, that the instructions contained therein are only a recommendation for the search engines and are demonstrably ignored. In addition, search engines can also access the excluded sites via other means, e.g. through backlinks. Using the “Disallow” function is therefore not a reliable way of excluding pages from crawling. On the contrary, if the robots.txt is used incorrectly, this can lead to major problems on search results pages.
In May 2019, Google updated its in-house Google Crawler to the current Chromium version 74. This is an important note as the predecessor was out of date and supported a few modern web technologies. The new crawler can now recognize modern SEO optimization and carry out better on-page analyzes.
URL structure, internal linking, and sitemap.xml are important SEO on-page factors
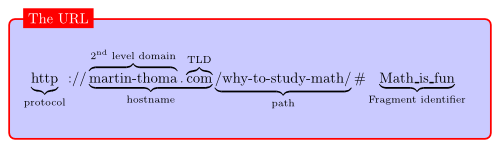
Next, you need to check the URL structure of your website. Questions are:
- Is it legible and clearly understandable for people?
- Can users read from this where they are on the website?
- Isn’t it too long?
The URL structure should not go beyond 5 hierarchy levels. This also goes hand in hand with the website structure. Today’s on-page SEO is not optimized for search engines, but for users. This means that the content has to be accessible easily and quickly. Too much cascading of the individual websites is therefore not advisable because it only leads to more hierarchies.
John Müller, the Webmaster Trends Analyst at Google, announced on May 3rd, 2019 via webmaster hangout that the internal linking of pages should be weighted even more than the URL structure.
The visible URLs are primarily relevant for the user experience. The internal linking of pages must instead be subject-relevant in order to achieve good on-page optimization. Siloing is also used in this context.
For good internal linking, you need to ensure that links are only made within one topic (silo). So should z. B. link all articles on the subject of web analysis to one another, but not to articles on the subject of SEO. For this you should always develop a linking concept and, especially in the case of links with JavaScript functionality, check whether crawlers can find the links and follow them.
If you have similar content, you should use the canonical tag. Imagine you run an online shop and offer a t-shirt in five colors. For each of these color variants, they offer a separate page with an individual URL.
In this case, you would have duplicate content on the domain because all pages would be textually identical and only differ in terms of color. With the canonical tag, you can now indicate on all pages which of the five URLs is actually relevant for search engines and which serve only as added value for the user.
In addition, you should provide search engines with the sitemap.xml file, which lists all URLs that are to be indexed. Therefore, this file must not contain any URLs that are set to “noindex” or are otherwise excluded from crawling or indexing.
Avoid duplicate content with SEO Onpage

The topic of duplicate content or duplicate content is one of the main focuses of SEO on-page optimization. The same pages can often be reached under several URLs. Classic examples are:
- URL with HTTP and https
- URL with www and without www
- URL with and without trailing slash
- URL with very similar content
For this reason, it is essential to set up redirects and to communicate very precisely to the search engines via canonical tag and sitemap.xml which web pages should really be indexed.
Imagine you run an online shop and offer a t-shirt in five colors. For each of these color variants, you create a separate page with an individual URL.
In this case, you have duplicate content on the domain because all pages are textually identical and only differ in terms of color. With the canonical tag, you can indicate on all pages which of the five URLs is actually relevant for search engines and which pages only serve as added value for the user.
In the case of forwarding, the user is automatically forwarded to the variant with https when calling up a URL with HTTP. This happens so quickly that he often doesn’t even notice.
Pagespeed – how fast is your website loading?

For several years now, Google has recorded more hits from mobile devices than from desktop devices. It is therefore important to offer a website that loads quickly. You can do this in several ways:
- They ensure small file sizes and short source codes. This optimizes the website overall and ensures a good user experience.
- You optimize the visible content through prioritized delivery of the source code. With this measure, the user sees the first content in the visible area long before the entire website has been loaded. This improves the perceived charging time.
- You change the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) to variant 2 (HTTP / 2). This is optimized for mobile devices and enables the parallel loading of various files as well as pre-loading of content. We also recommend the use of https for good on-page SEO.
Mobile optimization is becoming more and more important
In addition to the loading time, the presentation of the website on mobile devices must also be ensured. This is often done with a responsive design, which ensures that the website automatically adapts to the screen size of mobile devices. If you are planning a relaunch in the near future, you must definitely take this topic into account in your concept.
Structured data for good onsite marketing
With structured data, individual content is specifically marked for search engines. This can be company information, product information, recipes, events, or, more recently, FAQs. Overall, there are a lot of templates for the use of structured data on a website, but only relatively few are supported for Google optimization. The added value is that Google understands the content better and displays it separately on the search results page.
Further SEO on-page optimizations
The area of technical SEO also includes further measures such as progressive web apps, image markups or multilingualism. This is the “fine-tuning” in the area of technical SEO optimization. Therefore, these detailed topics are not elaborated on here.
Content optimization – the second step in on-page SEO

After the website has been improved under technical on-page SEO measures, you can now start optimizing your content. This is essentially divided into two areas:
Meta information: Optimize page title and meta description
The optimization of the page title and the meta description describes the optimization of the meta-information in Onpage SEO. The page title as an SEO criterion is particularly crucial, as it should contain the keyword and the brand. At the same time, it shouldn’t be too long to remain legible.
You will always see the page title in the tab of your browser as well as on the Google search results page.
The meta description is not SEO relevant in itself, but still has a large, indirect effect on onsite marketing. The meta description is displayed on the search results pages of the search engines if the content is appropriate. By addressing users directly with a call to action, you can improve the click rate on your hits and thus achieve a better ranking.
Content on the page itself – what can the user expect?
The actual content must meet the expectations of the user, otherwise, it will lead to high bounce rates. Note that you do not create the content for on-page optimization for search engines, but for users.
For this reason, Google places great emphasis on how legible the content is. In addition, the texts must be well structured and structured with headings. An increase in user interaction with the website is also desirable. You can achieve this through videos, pictures, picture galleries, comments, or the like.
It has been proven that a longer length of stay goes hand in hand with an increase in conversions.
If the content is very well created, Google may use it as a featured snippet. This is position 0 on the search results page, where Google answers a user’s question directly on the search results page.
Marketers have no control over the use of a featured snippet and therefore cannot predict when a snippet will be displayed and when not. To accommodate your own content in a featured snippet is therefore the supreme discipline of Google optimization for content.
Google Jobs – a whole new feature
With Google Jobs, the search engine giant introduced a completely new function in June 2019, which will lead to many on-page SEO optimizations in 2019. As soon as users google for a job title, they are shown a list of vacancies. After clicking on it, you will be redirected to the company’s website, where you can apply in the next step. To do this, website operators have to use structured data and use very specific content on the website.
Image Source – Wikimedia SEObility
Writer – Vishal Garg – Digital marketing company in Jaipur












Leave a Comment